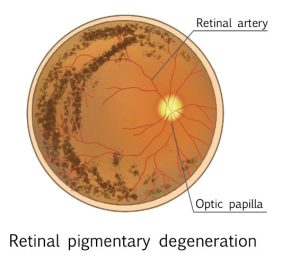
Because the disease progresses slowly, it is important to have regular checkups to monitor the progress of retinitis pigmentosa.
Funduscopic examination
Funduscopic examination is a method of assessment used to examine the fundus of the eye in detail by using eye drops to dilate the pupil.
In the early stages of the disease, the retina becomes discoloured.
In the middle stage, characteristic pigmentation appears in the peripheral area, and as the disease progresses, the degeneration of the retina spreads to the central part of the retina. Eventually, the macula also degenerates, and the optic disc has atrophy and turns pale.
Fluorescein angiography
Fluorescein angiography is a procedure that uses fluorescein to take pictures of the fundus of the eye. A yellow dye that fluoresces under cobalt blue light is injected intravenously. The fluorescence is more intense in areas with advanced retinal atrophy and is used to monitor the progression of the disease.
Visual field test
To check how much your field of vision has narrowed, you can take a test in which you press a button when you see a small light. With retinitis pigmentosa, your field of vision may become ring-shaped or partially lost. As the disease progresses, your field of vision narrows toward the center, as shown in the image below. This is called centripetal visual field constriction.

Electroretinogram
When light is absorbed in the retina, an electrical signal is generated, and an electroretinogram is a test that examines the response of electrical signal using electrodes placed on the cornea.
In the early stages of the disease, the response of electrical signals is weak, and in the middle or later stages, there is almost no response at all.
The test is performed under ophthalmic anesthesia and with contact lenses specially designed for the test, so it is principally painless.
Fundus autofluorescence
When there is a lot of a pigment called lipofuscin in the retina (retinal pigment epithelium), images appear brighter. However, as the disease progresses and the retinal pigment epithelium becomes damaged, the amount of lipofuscin decreases and images become darker.
While fluorescein angiography requires the injection of a contrast agent, fundus autofluorescence is a noninvasive procedure that is less stressful on the patient’s body.