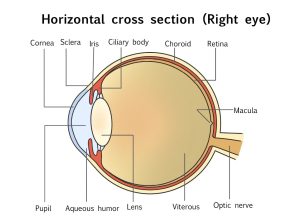
Information about the image on the retina is sent to the brain, which recognizes that a person has seen an object. By changing the thickness of the lens, you can see clearly whether it’s far or near.
As myopia progresses, the image is blurred out of focus on the retina in far-seeing even when the lens thickness is adjusted.
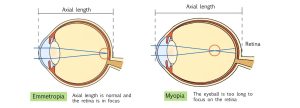
Myopia vs. emmetropia
When looking into the distance with no change in the thickness of the lens, the retina is correctly in focus, which is called emmetropia. On the other hand, with myopia, when looking at distant objects, they come into focus in front of the retina. On the retina, it is out of focus and therefore not clearly visible.
The more advanced the degree of myopia, the more difficult it is to see objects at greater distances.
Let’s look at how changes occur in the human eye from birth to growth.
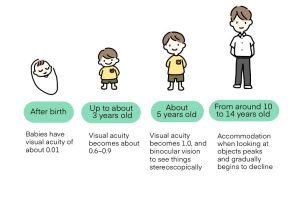
Newborns have small eyes, and the depth of the eyeball, called the (ocular) axial length, is about 17mm. Mild farsightedness happens when the focus is behind the retina.
As your body grows, so do your eyes, cornea and lens. As the eyeball grows larger, the axial length also becomes longer, and visual acuity grows to about 1.0 by around the age of 5. The axial length elongates to about 24 mm by the age of 16 and generally does not lengthen thereafter.
However, if only the axial length is elongated due to some effect, it becomes difficult to focus on the retina, resulting in myopia.
An increase of children with Myopia
According to school health statistics surveyed by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) in Japan, the number of elementary school students with naked eye visual acuity of less than 0.3 has increased approximately 4 times over the past 40 years. Many are presumed to have myopia.
| Year of study |
Elementary school Students (%) |
Junior high school Students (%) |
High school Students (%) |
| 1979 |
2.7 |
13.1 |
26.3 |
| 2010 |
7.6 |
22.3 |
25.9 |
| 2021 |
10.6 |
28.9 |
42.8 |
References: School Health Statistic Survey/2021 | MEXT in Japan
Perhaps due to the rapid penetration of smartphones over the past ten years or so, the percentage of children with myopia has increased in the last decades.
Myopia is a growing problem in many countries around the world, but it is especially noticeable in East Asian countries. In Singapore, it is said that 60% of schoolchildren aged 12 years are myopic, and there are also concerns about the negative effects of myopia by increasing the risk of various eye diseases in the future.
<Degree of myopia and susceptibility to eye disease>
| Degree of myopia |
Cataracts |
Glaucoma |
Retinal detachment |
Myopic macular disease |
| Low myopia
( -1 to -3D) |
1.8x |
1.6 x |
3.2x |
13.6x |
| Moderate myopia
( -3 to -6D) |
2.4x |
2.9x |
8.7x |
72.7x |
| High myopia
(> -6D >) |
2.9x |
12.6x |
845.1x |
Reference: The Complications of Myopia: A Review and Meta-Analysis” (Annechien E. G. Haarman)
D (diopter) is the refractive power and is a unit of measurement for the strength of myopia. The shorter the distance visible to the naked eye (focal length), the higher the value: -1D at a focal length of 1 m, -2D at a focal length of 50 cm, and so on. -6D or higher is referred to as a high degree of myopia.
Even with mild myopia, the risk of developing myopic maculopathy is approximately 14 times greater than with the absence of myopia. In order to maintain good vision throughout life, it is important to prevent the onset and progression of myopia in childhood.