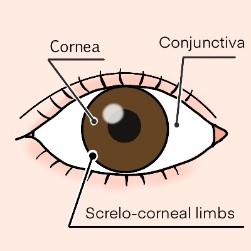
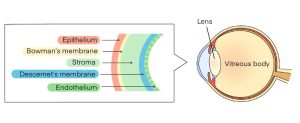
The causes and symptoms of corneal diseases vary depending on the location where they occur.
Corneal Epithelium Disorder
Corneal epitheliopathy is a condition in which the epithelium, the outermost layer of the cornea, is damaged, causing severe pain on the surface of the eye.
There are two types: superficial punctate keratitis, in which the epithelial defect is shallow and small, and corneal erosion, in which the wound reaches the entire thickness of the corneal epithelium. If the condition progresses further and the wound extends into the stroma or endothelium, a corneal ulcer or corneal perforation may result. Even mild symptoms of superficial punctate keratitis may cause glare, a sensation of a foreign body, and constant tearing.
As the condition progresses, you may experience eye pain, redness, eye discharge, and a white clouding of parts of the cornea.
The cornea is often damaged by fingernails, foreign objects, contact lenses, etc., but in cases of dry eye caused by dry indoor air or long hours of VDT work, the cornea is particularly susceptible to damage, so care must be taken.

Sleeping while wearing contact lenses can also cause corneal epithelial damage. In addition, eye drops, ultraviolet light, and welding light can also cause corneal epithelium disorder.
Corneal Endothelial Disorder
Once the cells of the corneal endothelium are damaged, they cannot regenerate. The corneal endothelium prevents water from entering the cornea, but as the number of cells decreases, water gradually enters the corneal layer, and the normally transparent cornea becomes cloudy. As corneal endothelial damage progresses, vision loss is seen due to edema of the cornea. As the disease progresses further, blistering and erosion in the epithelium occurs, which is often accompanied by severe pain.
This is called bullous keratopathy. In severe cases, an endothelial or corneal transplant (entire cornea) may be required.
In addition to trauma, other causes of endothelial damage include increased intraocular pressure due to a glaucoma attack or laser iridotomy. Other causes include contact lens use and aging.