Hordeolum is caused by a bacterial infection of the sebaceous or meibomian glands (also called tarsal glands) in the eyelid at the lash line.
They can cause inflammation and suppuration, and the area around the eyelid can become red, swollen, painful and itchy.
People usually call above condition stye, even though hordeolum is the formal name.
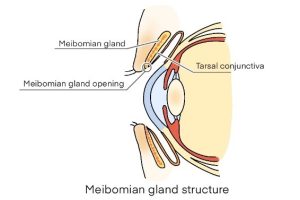
Role of the Meibomian Gland
Meibomian glands are located in the upper and lower eyelids and have small openings along the inside of the eyelash line. They are responsible for secreting oil.
The oil secreted by the meibomian glands covers the surface of tears, which moisturize the eyes and supply oxygen, creating an appropriate oil film. As a result, tears are resistant to evaporation.
Conversely, if the meibomian gland isn’t functioning properly, tears evaporate and the eye becomes dry, which can lead to dry eye.
What is Hordeolum
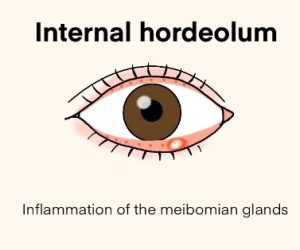
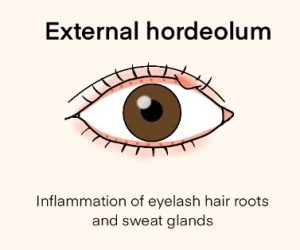
There are two main types of hordeolum. One is internal hordeolum, bacterial infection and inflammation of the meibomian glands on the inside of the eyelid. Another is external hordeolum, inflammation of sebaceous glands in the eyelash follicles.
Localized redness appears on the eyelid, often accompanied by mild pain and itching. As the inflammation worsens, the redness, swelling and pain increase. As suppuration progresses, pus accumulates in the swollen area. Once the pus is released, the condition begins to improve, but it is important to note that the condition can become severe.
The bacteria that causes this condition is mainly Staphylococcus aureus, which can cause an infection if you touch your eyes with contaminated fingers.
Staphylococcus aureus is found in the throat, nose, fingers, hair, etc. of healthy people. Normally, there is little risk of infection, but if your eyes are injured or your body’s immune system is weakened, symptoms are more likely to appear, so you need to be careful.
About Chalazion
Chalazions, like hordeolum, are common conditions caused by a blockage of the meibomian gland’s outlet, which leads to inflammation and the formation of fatty deposits called granulomas.
The main symptoms of chalazion are swelling of the eyelid and a foreign body sensation. However, in many cases, lumps may form on the inside of the eyelid without pain or redness. When accompanied by inflammation, the symptoms are similar to those of hordeolum (stye), and are called acute chalazion, which can be quite difficult to distinguish from hordeolum.
Note that leaving the area around the eye unclean with bacteria increases the likelihood of clogging of the meibomian glands.







