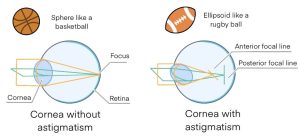
The cornea and crystalline lens refract incoming light and focus it to a single point. This lens enables the eye to see an image in focus.
When a patient develops astigmatism the cornea and lens becoming, disrupting incoming, resulting in blurred or double vision. Astigmatism can be sub-divided into two types: regular astigmatism and irregular astigmatism.
Regular Astigmatism
In regular astigmatism, the cornea or crystalline lens is distorted in one direction.
When the cornea or crystalline lens form oval shape like a rugby-ball, there is a flat curve in one direction and steep curve in the other direction, resulting in two focal lines as shown in the figure above.
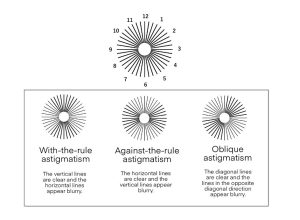
Astigmatism changes the images we see depending on whether the cornea or crystalline lens has a flat curve in the vertical, horizontal, or oblique direction. A characteristic symptom of regular astigmatism is that even if lines are clearly visible at a certain direction, lines that intersect in orthogonal direction are difficult to see.

With-the-rule astigmatism
This is caused when the meridian showing the strongest refraction is vertical. The image appears crushed vertically and vertical lines are clearly visible, but horizontal lines appear blurred. It’s the most common type of astigmatism, although it depends on the age of the patient.
Against-the-rule astigmatism
This is caused when the meridian showing the strongest refraction is horizontal. The image appears crushed horizontally, Against- the- rule astigmatism is the opposite of with-the-rule astigmatism, in which horizontal lines are clearly visible but vertical lines are difficult to see. The number of people who develop against-the-rule astigmatism increases with age.
Oblique astigmatism
A condition in which the axis of cornea or lens is oblique in shape. Certain oblique lines are easier to see, while lines oriented diagonally are difficult to see.
It’s also characterized by a tendency for objects to have a shadow which in some cases may be described by patients as double vision.
Irregular Astigmatism
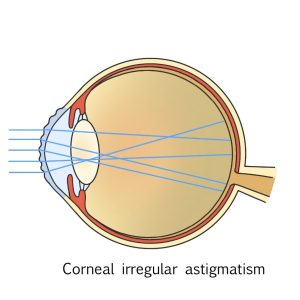
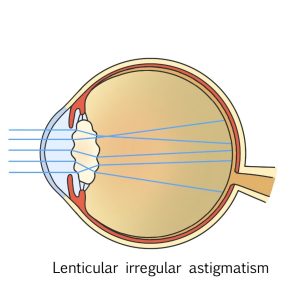
Irregular astigmatism describes a condition in which the corneal surface is irregularly distorted, or the crystalline lens is distorted which prevents images from being properly focused.
When one eye with irregular astigmatism looks at an object, see an image with multiple layers of blur.
It’s caused by damage to the cornea or partial hardening of the lens during the early stages of cataracts.