Environmental
Climate Change
Response to Climate Change
In 2021, the HOYA Group identified four material issues. Among these, the entire Group is tackling “reduction of greenhouse gases” as a top-priority issue. In December 2021, the Group endorsed the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). Pursuant to this announcement, in April 2023, the Group began disclosing information based on the TCFD Declaration, strengthening its response to risks associated with climate change. In February 2023, the Group joined RE100, an international environmental initiative aimed at achieving 100% sourcing of renewable energy for all energy consumed in business activities. The HOYA Group aims to reach this milestone by fiscal 2040 and is accelerating its efforts toward that end.


Medium- to long-term Targets and Results
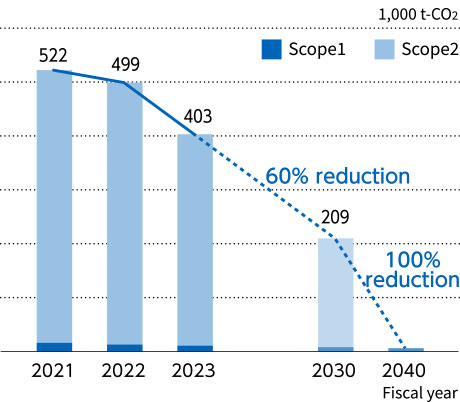
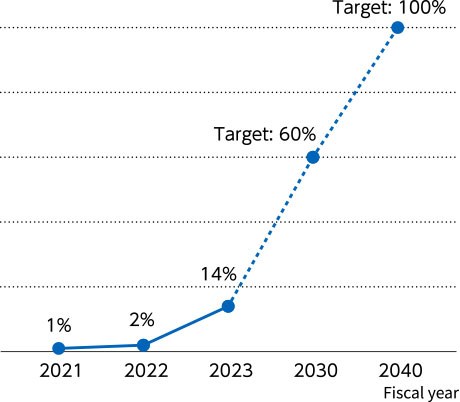
Over 90% of the HOYA Group’s greenhouse-gas emissions (total of Scope 1 and Scope 2) are in Scope 2; the majority of these are indirect emissions arising from purchased electrical power. By aggressively advancing the transition to electricity from renewable sources that do not emit greenhouse gases, the Group is effectively slashing CO2 emissions. The Group is targeting complete transition to renewables (renewable-energy usage rate of 100%) by fiscal 2040, with an interim target of 60% renewable-energy usage rate by fiscal 2030.
In line with the Company’s goals, each business division is developing and implementing medium- to long-term roadmaps for the introduction of renewable energy and CO2 reduction measures. The entire Group is working together to achieve these objectives.
CO2 Emissions
Renewable-energy usage rate
*1 Since fiscal 2021, greenhouse gas emissions (Scope 1 and Scope 2, energy consumption) have been verified by a third party through limited-assurance operations. In the course of the verification process, the method of calculation and coefficient used to calculate CO2 were revised, resulting in correction of the figures disclosed in February 2023. The Group expects to receive third-party verification of the fiscal 2023 results within the current year.
*2 From fiscal 2023, estimates for smaller sites for which actual data have not been collected are included in the total (about 4% of the total).
*3 The Group is considering offsets using carbon credits for the residual emissions after maximum reduction efforts are made for Scope 1.
For data on Scope 1 and Scope 2 results, please refer to the Environment page of the ESG Databook.
Introduction of Renewable Energy
The HOYA Group is moving forward with switching to renewable energy at each production and sales site. In fiscal 2023, the number of production sites with solar panels increased to four from one, and the Group is also accelerating conversion to purchase of renewable energy by reviewing electrical-power agreements and using energy attribute certificates, focusing on countries in which renewables are readily available. The Vision Care Division has achieved virtually 100% renewable energy use at the Matsushima Plant and all other domestic production sites in Japan and several production sites in Europe (Hungary, Germany, and Italy). In addition, all Eye City contact lens stores (including offices) and HOYA Global head office (Japan) have already achieved 100% renewable-energy usage, by means of non-fossil-fuel certificates from FIT. We will place more importance on the perspective of introducing renewable energy power with additionality and will actively promote initiatives to achieve the goal.

Solar panels installed at HOYA Optical Technology (Weihai) Co., Ltd. (annual generating capacity: 1,300 MWh; reduction in annual CO2 emissions: about 800 t-CO2)

Solar panels installed at HOYA LAMPUN LTD. (Annual generating capacity: about 2,200 MWh; Annual CO2 reduction volume: about 1,000 t-CO2)
Energy saving and power saving activities
At production bases, we are replacing facilities with energy-saving types (such as adopting ice thermal storage systems and high-efficiency transformers), conducting energy-saving activities (such as optimizing the operating hours of boilers and air-conditioning equipment) and promoting roof-greening, etc. We are also endeavoring to suppress CO2 emissions from non-production bases by such means as introducing casual wear, adjusting the indoor temperature appropriately and implementing efficient lighting in offices.
Examples of energy/power saving initiatives
Use of the Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM)
-
In 2016, we introduced a heat recovery heat pump at the eyeglass lens plant in Vietnam. It is used to save energy and reduce CO2 emissions by using the heat that used to be expelled to the outside air when cold heat was supplied as a source of cold heat for the production process and as an auxiliary heat source for heating the water used in the manufacturing process. Before introducing the heat recovery heat pump, we used only electric heaters to obtain the desired temperature.
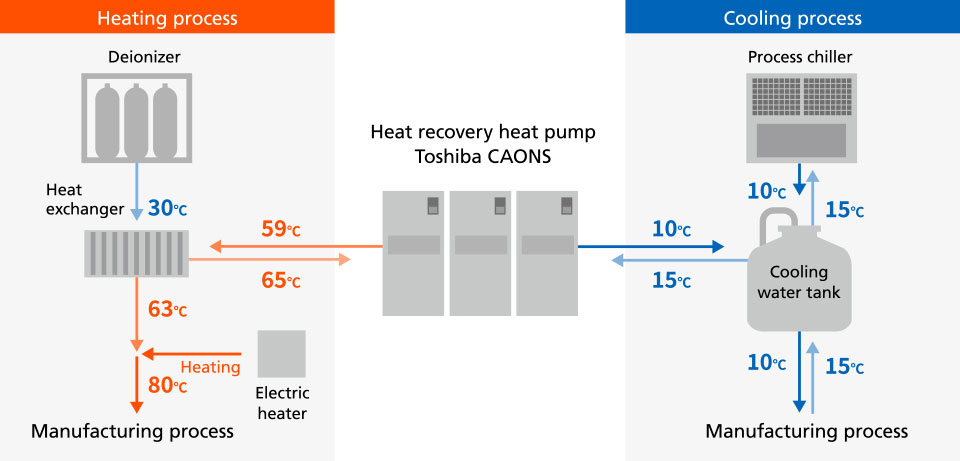
At the eyeglass lens plant in Vietnam, one of the existing centrifugal chillers was replaced with a highly efficient inverter centrifugal chiller. By using the new chiller for regular operation and the old one as backup equipment, we achieved a lower introduction cost, improved energy efficiency, and reduced CO2 emissions at the same time.
Scope 3
The HOYA Group started to calculate Scope 3 emissions in fiscal 2023 as a first step to reduce CO2 emissions in the entire supply chain. First, all relevant categories were calculated for the first two business divisions based on fiscal 2022 data, then categories that were major sources of emissions were identified and company-wide calculations were performed for the major categories.
In the future, we will expand the scope of data collection to include calculation of all relevant categories, improve the efficiency of data collection work and measurement accuracy, and promote engagement with related companies in the supply chain to contribute to a sustainable society and reduce emissions. We also aim to obtain SBT (Science Based Target) certification as we move forward with Scope 3 reduction initiatives.
Scope 3 Category |
1,000t-CO2 |
|
|---|---|---|
C1 |
Purchased goods and services |
567 |
C2 |
Capital goods |
18 |
C3 |
Fuel and energy related activities (not included in scope 1 or 2) |
67 |
C4 |
Upstream transportation |
49 |
C5 |
Waste generated in operations |
13 |
Scope of calculation
・Businesses in scope: Global data for 12 major businesses and the head office
・Only mass-production plants are in scope for the Vision Care Division (eyeglass lenses)
・Upstream transportation of C4 is calculated for procurement logistics regardless of whether the HOYA Group is the consigner.
Scenario Analysis Based on the TCFD Declaration
From fiscal 2022, the HOYA Group began scenario analysis based on the TCFD recommendations. In the first year, the Group focused on plants in Thailand and Vietnam that are its main production sites for two business divisions, eyeglass lenses and glass substrates for HDDs, as these operations have high CO2 emissions (high power consumption). Two scenarios were drawn up with fiscal 2030 as the middle of the timeline: one in which global temperatures increase by 4°C, another in which they increase by 1.5°C. In fiscal 2023, the scope of analysis was widened to include the Optics Division (optical lenses). The combined CO2 emissions of these three business divisions account for 88% of the HOYA Group's total CO2 emissions. We also conducted a risk assessment of all our production sites with respect to physical risk (flooding), which we consider to be a key climate change risk. The HOYA Group will continue to conduct regular reviews in response to changes in the external environment, reflecting the results of scenario analysis in its business activities and advancing responses to risks and opportunity. In this way the Group will enhance its resilience to climate change.
For details, please refer to “TCFD Disclosure.”
Examples of risks and opportunities in the eyeglass lenses business division (excerpt from moderate or higher risks)
Description |
Response |
|
|---|---|---|
Transition risks |
・Delays in responding to consumers’ heightened awareness of climate change results in lost market share and/or declining sales. ・Action on climate change and climate-related disclosure have been added to factors customers use to select suppliers. Delay in responding results in lost customers and/or declining sales. ・Inadequate response to environmental issues such as reduction of CO2 emissions and water recycling causes loss of reputation and/or declining sales. |
・Consideration of listing CO2 emissions on product packaging ・Revision of marketing strategy: Reduction of impact from climate change through product innovation; enhanced dissemination of information ・Regular reporting to customers and other external stakeholders regarding progress on ESG ・Expansion of disclosure related to climate change, such as TCFD or the Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) |
Physical risks |
Infectious-disease outbreaks made possible by unusual weather disrupt production activities and supply chains or trigger lockdowns and other restrictions on activity, causing the optometrist shops that are the Group’s customers to restrict hours of operation, thereby reducing demand. |
・Drafting and updating of BCPs for Group plants ・Geographical diversification of production sites |
Unusual weather causes stagnation in production or sales activities; flooding causes inundation or destruction of production sites. |
・Geographical diversification of production sites and advancement of measures against water damage ・Drafting of BCPs to secure/safeguard materials, inventories, etc. |
|
Opportunities |
As demand for low-carbon products grows, early success in product development leads to increased sales. |
・Listing of carbon footprints ・Incorporation of determination to reduce environmental impact into product development strategy ・Coordination with material producers |
As demand grows for products that are easy to recycle/reuse, early success in product development leads to increased sales. |
・Formation of a product strategy focused on a recycling-oriented society through collaboration with suppliers and customers |
|
The Group streamlines production processes using DX, etc. |
・Reduction of CO2 emissions and related costs by improving production efficiency ・Investment in DX and DX training |
|
Drafting of BCPs, use of in-house production sites and diversification of suppliers |
・Introduction of and training in BCPs ・Refurbishment of each plant, geographical diversification of production sites, etc. |
Examples of risks and opportunities in the glass substrate for HDDs business division (excerpt from moderate or higher risks)
Description |
Response |
|
|---|---|---|
Physical risks |
Infectious-disease outbreaks made possible by unusual weather disrupt production activities and supply chains, causing customers’ plants to reduce levels of operation, thereby reducing demand. |
・Drafting and updating of BCPs for in-house production sites ・Geographical diversification of production sites ・Consideration of plans to reduce customers’ climate-change risk |
Opportunities |
Disclosures on ESG, climate change, etc. boost the Company’s reputation in financial markets, reducing cost of fundraising. |
・Deployment in disclosures for TCFD and on ESG ・Disclosure and improvement of rank on CDP |
As demand for low-carbon products grows, early success in product development leads to increased sales. |
・Listing of carbon footprints ・Revision of product strategies ・Increase in budget for technology development ・Coordination with material producers |
|
As global warming causes water shortages, successful development of technologies to reuse and reduce water use leads to reduced water costs. |
・Establishment of production methods that use little water ・Introduction of advanced water treatment technologies, increase in reuse |
|
Technologies such as DX achieve improved efficiency in manufacturing processes. |
・Reduction of CO2 emissions and reduction of related costs due to improved production efficiency ・Investment in DX and DX training |
|
Drafting of BCPs, use of in-house production sites and diversification of suppliers |
・Introduction of and training in BCPs ・Refurbishment of each plant, geographical diversification of production sites, etc. |
Examples of risks and opportunities in the Optical Glass Business Division (excerpt from moderate or higher risks)
Description |
Response |
|
|---|---|---|
Physical risks |
Delays in deliveries and reduced production volume due to stoppages of operations at raw material suppliers caused by extreme weather and natural disasters |
Securing inventory (especially for critical materials for which procurement sources are limited) |
Securing multiple suppliers for critical materials |
||
Production activities and supply chain disruptions caused by outbreaks of infectious diseases triggered by extreme weather conditions, and a decline in demand due to a downturn in the operation of factories by customers |
Formulation/update of BCP for our factories |
|
Establishment of production backup systems at other sites |
||
Stagnation of production and sales activities due to extreme weather conditions, and the submersion or destruction of production sites due to flooding |
Promote production backup systems at other sites and measures against flood at each site |
|
Formulate BCP including securing materials and inventory |
Risk Management
The HOYA Group continually monitors conditions related to climate change. If conditions change significantly, the head office TCFD Project, which includes members of the ESG Promotion Office, the Corporate Communication Department and the Environmental Safety and Hygiene Department, works with business divisions to review risks. Under the general supervision of the persons responsible for each business, the appropriate segments of each business division (Production Division, Retail Development Department, Purchasing Department, etc.) coordinate and conduct their responses.
With respect to risk related to changes in the operating environment due to climate change (transition risks), based on scenario analysis, the sustainability/ESG teams and persons responsible in the business divisions in each country work with segments related to sustainability, such as environmental, quality-assurance, purchasing and other segments, to draft and implement responses appropriate to their respective business divisions.
Flooding risk assessment
Increased and severe natural disasters, outbreaks of infectious diseases, and water shortages due to climate change may affect not only our own operations but also those of our supply chain, including raw material procurement and the production and sales activities of our customers. The HOYA Group assesses flood risk and water stress risk at production sites by using the Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas tool developed by the World Resources Institute (WRI), an international environmental NGO, and by conducting interviews at production sites. In order to conduct efficient corporate operations from a global perspective, the Group promotes management decision-making, R&D, production, and sales in optimal locations, and in particular, its production sites are located mainly in Southeast Asia. The results of the risk assessment showed that the flood risk was relatively high for production sites in Southeast Asia, including Vietnam, Thailand, and Indonesia. Sites identified as high risk collaborate with the Environment, Health and Safety Department at the head office to formulate countermeasures and implement them as priorities.
Countermeasures against flooding
Based on the experience of flood damage at the Vision Care Thailand production site in 2011, we are promoting the establishment and periodic review of flood countermeasures and business continuity plans (BCP) at each production site, as well as the development and training of systems to ensure the safety of employees.
We are also working to reduce risk by decentralizing our production sites to areas with relatively low risk of flooding and securing appropriate inventories in case of supply chain disruptions.
Infection control measures
Since before the COVID-19 pandemic, HOYA had been proactively working on measures to address the risks of emerging infectious diseases, following the formulation of its “Guidelines on Countermeasures Against New Strains of Influenza and Other Infectious Diseases” based on a scenario of pandemics of new strains of influenza and other emerging infectious diseases. Under the Guidelines, we have established the HOYA Group Influenza/Epidemic Risk Management Team, formulated a BCP, and organized channels for collecting, conveying and sharing information; in addition, we have put in place a framework to enable the stable supply of products, etc. while minimizing health hazards by giving top priority to ensuring the safety of employees, their families, relevant parties and others.
Indicators and Targets
Indicators used to evaluate climate-related risks and opportunities include Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions and share of renewables in energy used in business activities.
Targets for introduction of renewable energy
・Transition to 60% of electricity used in business activities to renewable energy sources by fiscal 2030
・Transition to 100% of electricity used in business activities to renewable energy sources by fiscal 2040
CO2emission reduction targets (Scope 1 and Scope 2)
・60% reduction of CO2 emissions by fiscal 2030 (compared with fiscal 2021)
・100% elimination of CO2 emissions by fiscal 2040 (compared with fiscal 2021)
Biodiversity

Afforestation area in Vietnam
The HOYA Group works actively to support and protect biodiversity. Based on its Environmental Philosophy and Fundamental Environmental Policies, the Group scrupulously conducts appropriate management of water use, wastewater, waste materials and chemical substances, as well as cleanup activities in the regions in which its production sites are located, in Japan and overseas. In August 2022, the HOYA Group began participating in the JAL Carbon Offset Program*. Through this program, the Group offsets the CO2 it emits on business flights to or from Japan on JAL with carbon credits purchased from the Southern Cardamom and Amazon Rainforest Conservation Projects. Preserving the rainforest provides vital regional protection, as it not only preserves a “carbon sink” that absorbs CO2 but also protects wildlife, supports biodiversity, and supports the livelihoods of local residents. By purchasing these carbon credits, the HOYA Group supports this project. In fiscal 2023, the Group purchased credits equivalent to some 152 tons of CO2.
In addition, linking efforts to protect biodiversity with employee health promotion programs, we are planting trees in Southeast Asia in a program where the number of trees planted matches the total number of steps taken by all participants. In partnership with the Japan International Forestry Promotion and Cooperation Center, the HOYA Group has been planting and caring for trees in planting areas in Vietnam as well as providing technical education on afforestation to local residents. In fiscal 2023, Group employees contributed to the planting of 1.4 ha of trees (approximately 9,000 trees).
*This carbon project is verified through the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS).
